Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) occurs when pressure inside the eye increases. This happens due to an imbalance in the production and drainage of aqueous humor, the clear fluid that fills the eye’s front portion. Normally, aqueous humor flows in and out to maintain balanced pressure. When drainage fails, elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) develops. High IOP can damage the optic nerve, leading to vision loss or blindness, especially in glaucoma cases.
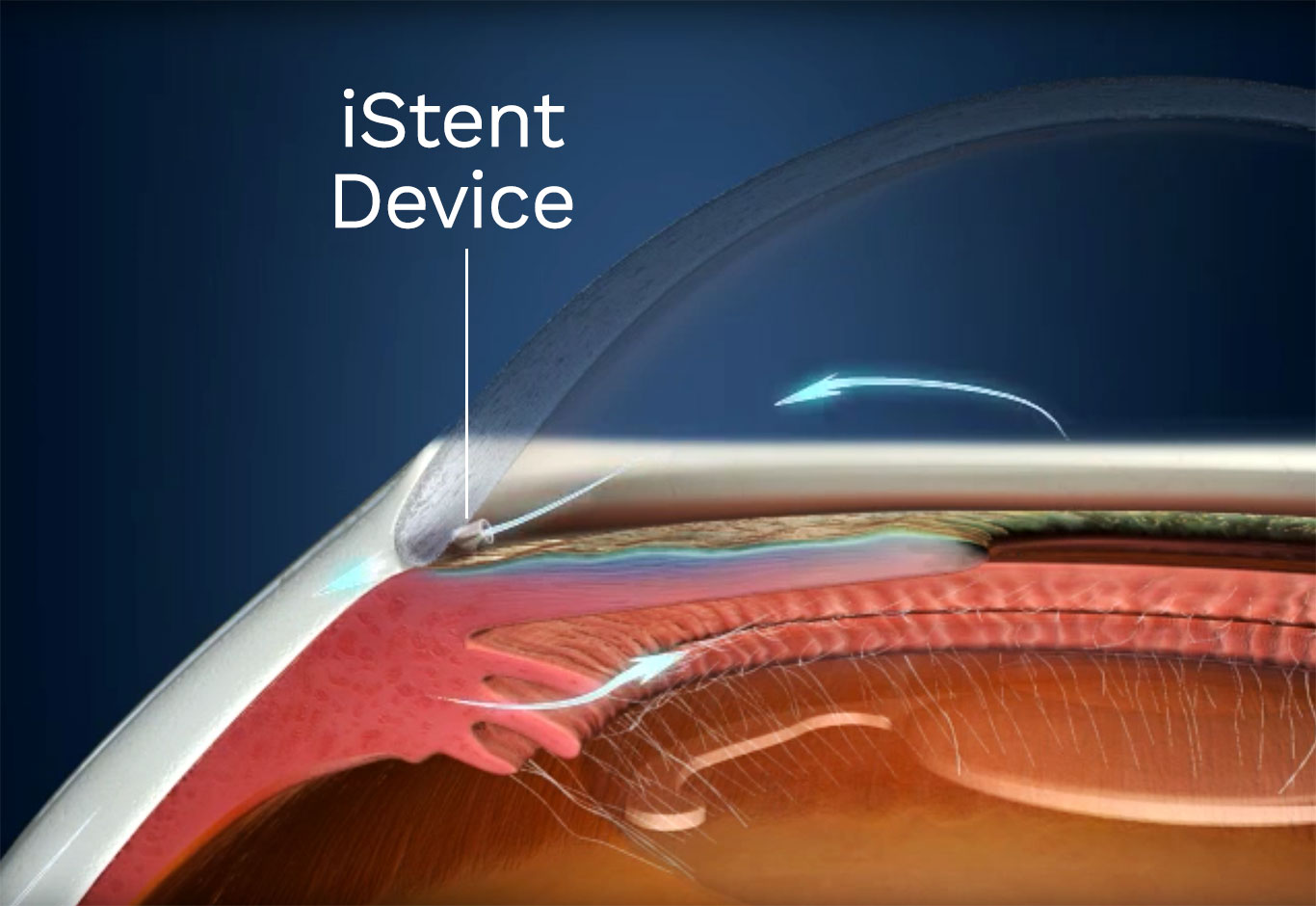
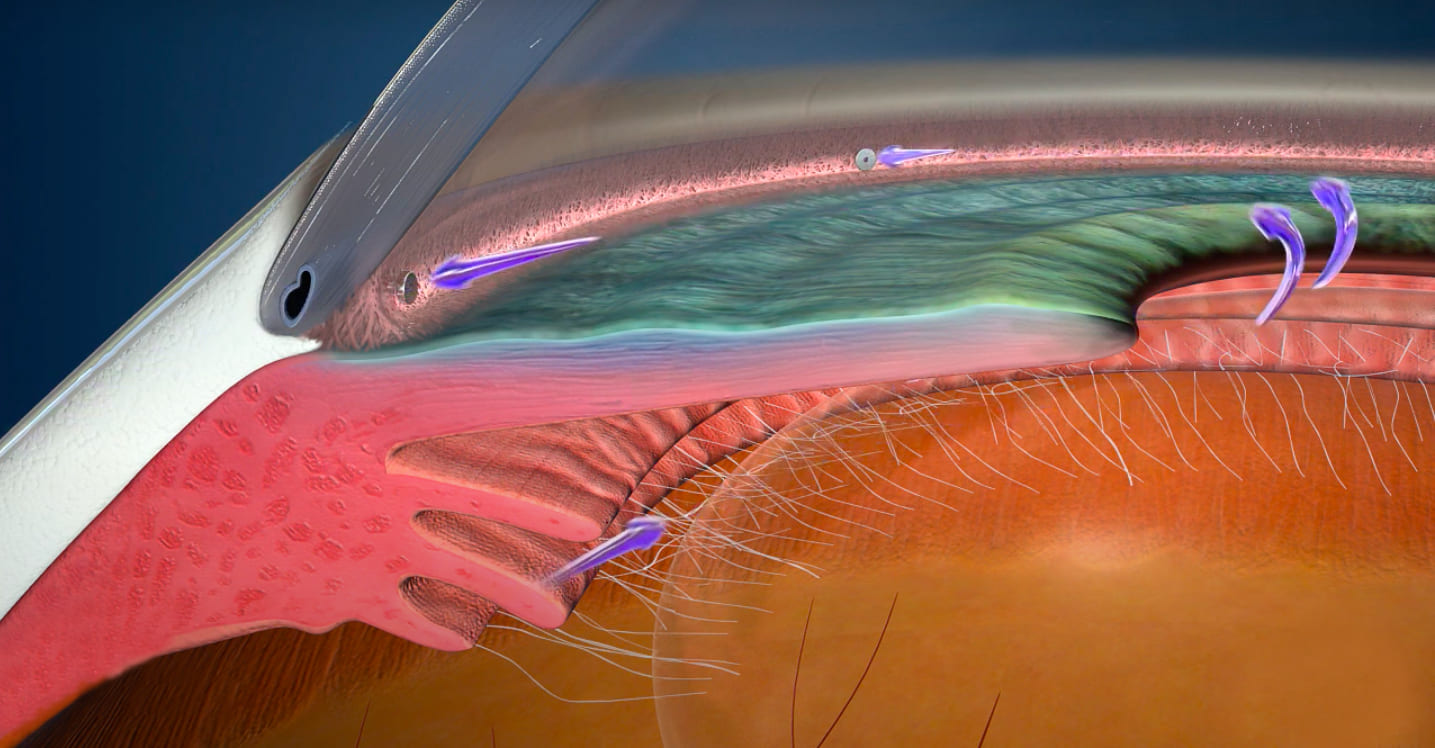
Minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS) includes procedures that lower IOP in glaucoma patients. These surgeries are less invasive than traditional glaucoma treatments. They often allow for faster recovery and fewer side effects.
Some common MIGS procedures include:
- Placing a stent to bypass the trabecular meshwork
- Removing trabecular meshwork tissue to improve drainage
- Enhancing aqueous outflow through Schlemm’s canal
- Increasing aqueous outflow via the suprachoroidal space
- Reducing aqueous production by ablating the ciliary body
Not all MIGS procedures suit every patient. An eye exam and consultation with a specialist help determine the best treatment.