Navigating Simultaneous Bilateral Cataract Surgery: The Ins and Outs
Simultaneous Bilateral Cataract Surgery (SBCS), also known as Immediately Sequential Bilateral Cataract Surgery, is a procedure that has sparked debates in the medical community. While studies suggest its safety and efficacy, the decision to opt for simultaneous surgery involves weighing the advantages and disadvantages.

Advantages:
Efficiency and Convenience:
- Minimizes patient visits, reducing the burden on surgical facilities and doctor’s offices.
- Faster recovery to binocular vision, especially beneficial for patients with high refractive errors.
- Decreased cost to both patients and the healthcare system.
Faster Recovery:
- Streamlining the surgical process can lead to quicker recovery times for patients.
Disadvantages:
Risk Factors:
- Potential risks of bilateral endophthalmitis and toxic anterior shock syndrome (TASS) pose concerns.
- Inability to gain refractive insight from the first eye may impact the overall outcome.
- Physicians may face decreased reimbursement in certain healthcare systems.
Regional Variations:
- Varying perspectives on SBCS are evident globally, with Sweden embracing it more widely than the United States.
Patient Selection:
Historical Practice:
- Doctors historically performed SBCS on select patients, including those with serious co-morbidities.
- Examples include patients with Down Syndrome who face challenges with transportation and anesthesia.
Current Trends:
- Today, SBCS is offered to routine, healthy patients as a convenience and cost-saving measure.
Indications:
Bilateral Cataracts:
- SBCS is typically indicated when both eyes require cataract surgery.
Contraindications:
Risk Factors:
- Any factors increasing the risk of surgical complications, endophthalmitis, or TASS.
- Conditions like untreated blepharitis, mucocele, diabetes mellitus, immunosuppression, iodine allergy, and corneal abnormalities may contraindicate SBCS.
Eye-specific Factors:
- Conditions like high myopia, high hyperopia, lenticular abnormalities, glaucoma, and previous laser refractive surgery may pose contraindications.
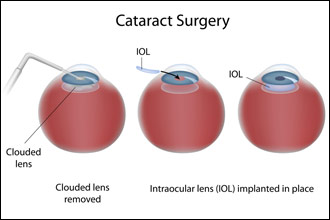
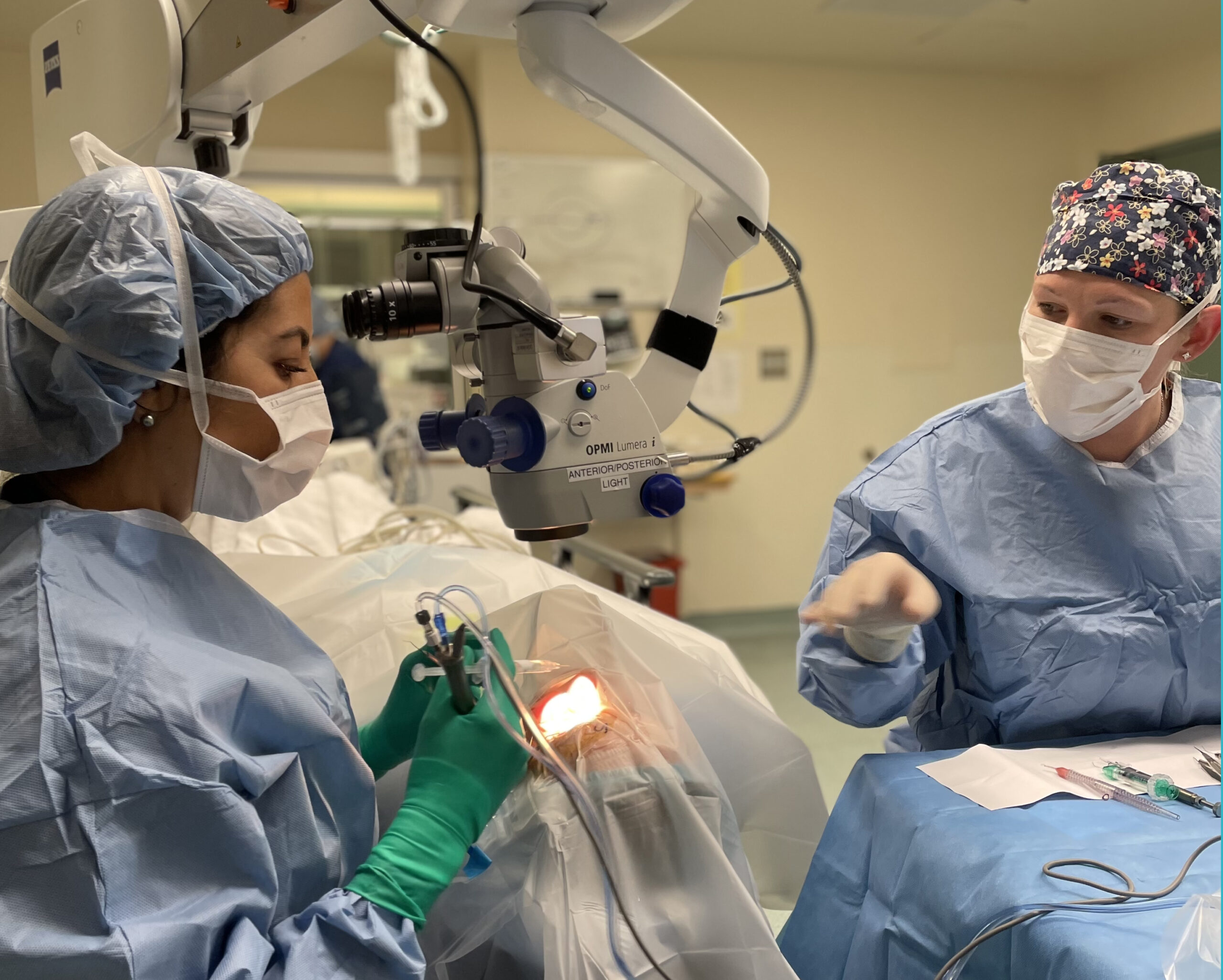
Surgical Technique:
Independent Operations:
- Involves performing bilateral cataract extraction with intraocular lens placement as independent operations on the same visit.
- Patient re-prepping and draping occur between eyes.
 Outcomes:
Outcomes:
Comparable Results:
- Recent studies indicate no significant difference in outcomes between SBCS and traditional sequential cataract surgery.
Complications:
Risk Awareness:
- Potential complications include bilateral endophthalmitis, TASS, and refractive surprises.
- Diligent preoperative evaluations and risk assessments are crucial to minimize complications.
Conclusion:
Simultaneous Bilateral Cataract Surgery presents a nuanced landscape with benefits and risks. As technology and techniques advance, the debate around its widespread adoption continues. Patient-specific factors, regional practices, and careful consideration of contraindications play vital roles in the decision-making process.




 Outcomes:
Outcomes:
