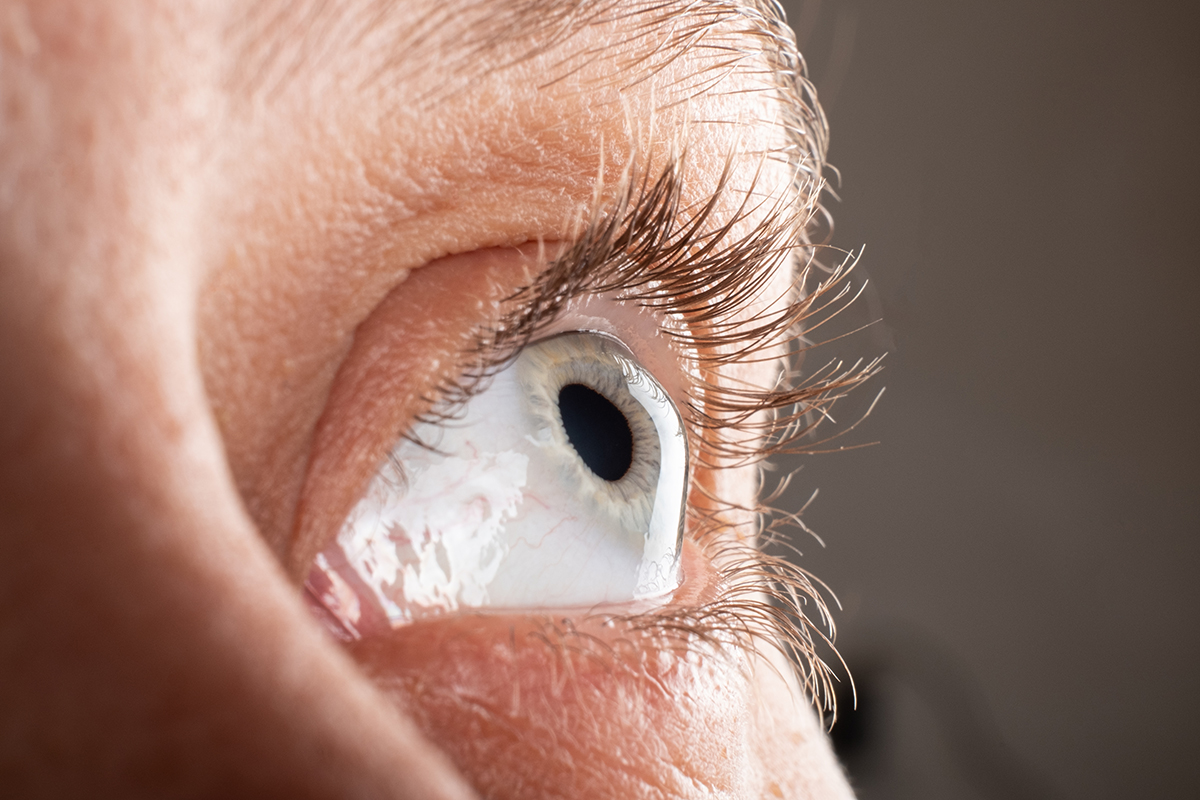
Keratoconus is an eye condition that causes progressive thinning of the cornea, resulting in blurred vision. Although researchers do not yet fully understand its exact etiology, they believe it is likely secondary to oxidative stress. This stress disrupts the balance between collagen production and destruction and may also lead to a deficiency of the cells that stabilize the anterior layers of the cornea.
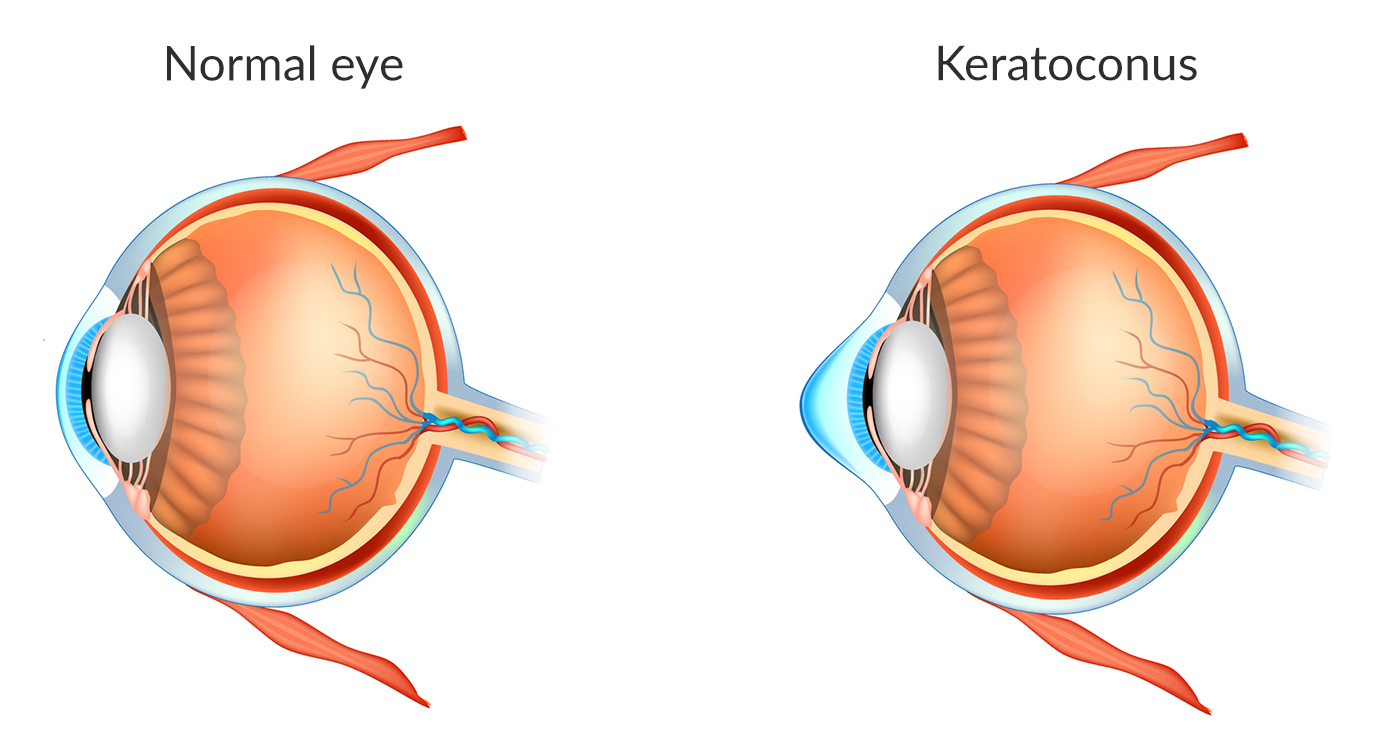
Normal Cornea and Keratoconus (KC) Cornea
Several factors increase the risk of developing keratoconus. For instance, individuals with a family history of the condition, Down’s Syndrome, or chronic eye allergies have a higher likelihood of experiencing it. Additionally, people who frequently rub their eyes face an increased risk. Researchers have also suggested a possible link between hormonal changes and keratoconus, but this relationship remains controversial.
Doctors usually diagnose keratoconus at a young age. Patients often report symptoms such as cloudy vision, ghosting objects, eye strain, and sensitivity to bright lights. Moreover, they frequently require changes in their glasses prescription, especially due to worsening astigmatism.
To confirm the diagnosis, an eye care provider conducts a comprehensive eye exam. They also perform ancillary tests, including corneal topography and measurements of the corneal thickness pattern, to assess the condition more accurately.

Corneal topography
Treatment options depend on the stage of keratoconus. Initially, corrective glasses or soft contact lenses may be sufficient. However, as the condition progresses, rigid contact lenses, hybrid contact lenses, collagen cross-linking, corneal transplantation, and corneal rings may be necessary.
Facts:
- Symptoms start usually at a young age.
- It is the leading cause of corneal transplant in the US.
- It is a bilateral disease but commonly asymmetrical in its symptoms.